A new book with focus on paleoseismology has been published by GSA. Special Paper 479 – “Geological Criteria for Evaluating Seismicity Revisited: Forty Years of Paleoseismic Investigations and the Natural Record of Past Earthquakes” is edited by Franck A. Audemard M., Alessandro Maria Michetti and James P. McCalpin. Again, a lot of interesting reading stuff for your flight to Corinth…
Posts in the category » « ( 280 Posts )
-
GSA Special Paper 479 – Geological Criteria for Evaluating Seismicity Revisited: Forty Years of Paleoseismic Investigations and the Natural Record of Past Earthquakes
2011-08-29 | in Paper -
Special issue on Archaeology and Paleoseismology in Quat. Int. 242
2011-08-22 | in Paper | 2 responsesIt is our greatest pleasure to announce that a new special issue on paleo- and archaeoseismology has been published. The special issue of Quaternary International mainly consists of contributions from a selection of those presented during the first International Workshop on Earthquake Archaeology and Palaeoseismology held at the ancient Roman City of Baelo Claudia (South Spain) in September 2009. There in Southern Spain, the first joint meeting of the INQUA Focus Area on Palaeoseismology and Active tectonics and the UNESCO-IUGS programme IGCP567 on Earthquake Archaeology took place. This volume is one of the first accounts of an integrated approach in the study of past earthquakes combining recent advances in palaeoseismology and earthquake archaeology.
There’s a lot of great reading stuff or the summer holidays or on the plane to Corinth… more
-
New paper on active tectonics at Lake Ohrid
2011-08-03 | in PaperOur new paper on lake Ohrid was published in the ZDGG: Reicherter, K., Hoffmann, N., Lindhorst, K., Krastel, S., Fernandez-Steeger, T.M., Grützner, C., Wiatr, T. 2011. Active basins and neotectonics: morphotectonics of the Lake Ohrid Basin (FYROM and Albania). Z. dt. Ges. Geowiss 162 (2), 217 -234. more
-
The Wednesday Centerfault (5)
2011-06-01 | in CenterfaultAfter we dealt with some faults in Greece, let’s move to Spain. The Ventas de Zafarraya Fault (VZF) west of the Granada basin (36.96° N, 4.14°W) has a beautiful morphologic expression and an exciting history. The fault bounds the Zafarraya polje to the south, with Quaternary sediments to the north (hanging wall) and limestones of the Internal Subbetics in the footwall. more
-
New paper on the paleoseismicity of the Dead Sea – Kagan et al., 2011
2011-04-28 | in PaperSome days ago a new paper on the paleoseismicity of the Dead Sea area during the late Holocene has been published in JGR. Kagan et al, 2011 investigated two new study sites in the northern and southern parts of the Dead Sea Basin and compared the seismites found there with the information of the Ein Gedi core presented by Migowski et al., 2004.
-
The Wednesday Centerfault (1)
2011-04-27 | in CenterfaultIt’s not easy to prepare weekly Friday links when you are abroad, this is what I had to realize in April. However, I will try to post a natural beauty each Wednesday in the future, the Wednesday Centerfaults and Centerfolds.
Today, I start with the Kaparelli Fault in Greece (38.22°N, 23.23°E). This beautiful limestone fault scarp is more than 2.5 km long and up to 5 m high. The fault was activated during the 1981 Corinth earthquakes. more
-
New paper: Alsop & Marco: Soft-Sediment deformation within seismogenic slumps of the Dead Sea Basin
2011-04-17 | in PaperSome days ago, a great new paper was published on the investigation of soft-sediment deformation in paleoseismology: “Alsop & Marco 2011: Soft-Sediment deformation within seismogenic slumps of the Dead Sea Basin. Journal of Structural Geology 33 (2011) 433-457.” The authors investigated the most beautiful seismites I’ve ever seen and generated different scenarios for their interpretation with respect to paleoseismic events. more
-
Friday’s earthquake and Darwin gap
2011-02-15 | in PaperA nice short discussion about the Lorito et al., 2011 paper regarding the seismic gap at the Chilean coast and seismic slip during the 2010 earthquake, can be found at Highly Allochthonous. The discussion highlights the paper findings under the glance of the recent Bio-Bio earthquake from Friday, which took place in this so called Darwin gap.
-
Searching for Records of Past Earthquakes Under Water
2011-02-08 | in Paper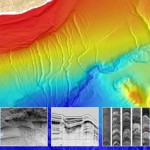 In its latest issue, EOS reports on the European Science Foundation conference “Submarine Paleoseismology – The Offshore Search of Large Holocene Earthquakes” which was held in Obergurgl, Austria from 11-16 September 2010.
In its latest issue, EOS reports on the European Science Foundation conference “Submarine Paleoseismology – The Offshore Search of Large Holocene Earthquakes” which was held in Obergurgl, Austria from 11-16 September 2010. -
What’s up? The Friday links (5).
2011-02-04 | in The Friday Links The Accredtionary Wedge #30 blog carnival hosted by Mountain Beltway came up with a tasting idea in January: The Geological Bake Sale. Explore and enjoy thematic food like the moon surface cake, the pillow lava bread and the debris flow vegetables. If you create a sweet fault or a tasty trench, we promise to publish it on paleoseismicity.org. more
The Accredtionary Wedge #30 blog carnival hosted by Mountain Beltway came up with a tasting idea in January: The Geological Bake Sale. Explore and enjoy thematic food like the moon surface cake, the pillow lava bread and the debris flow vegetables. If you create a sweet fault or a tasty trench, we promise to publish it on paleoseismicity.org. more
